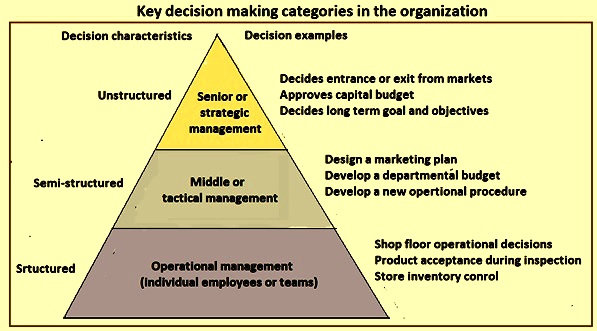
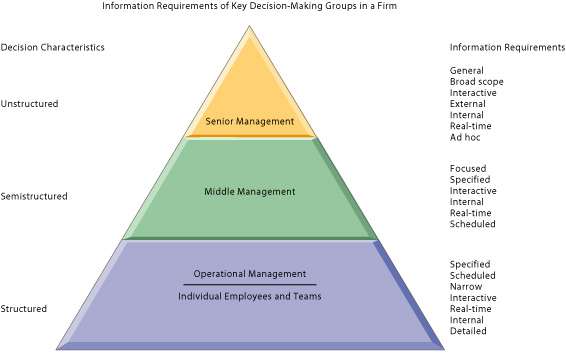
Structured Decision Making Is Most Prevalent at Senior Organizational Levels.
In this form one parent company owns subsidiary companies each of which uses its brand and name. A TRUE B FALSE.
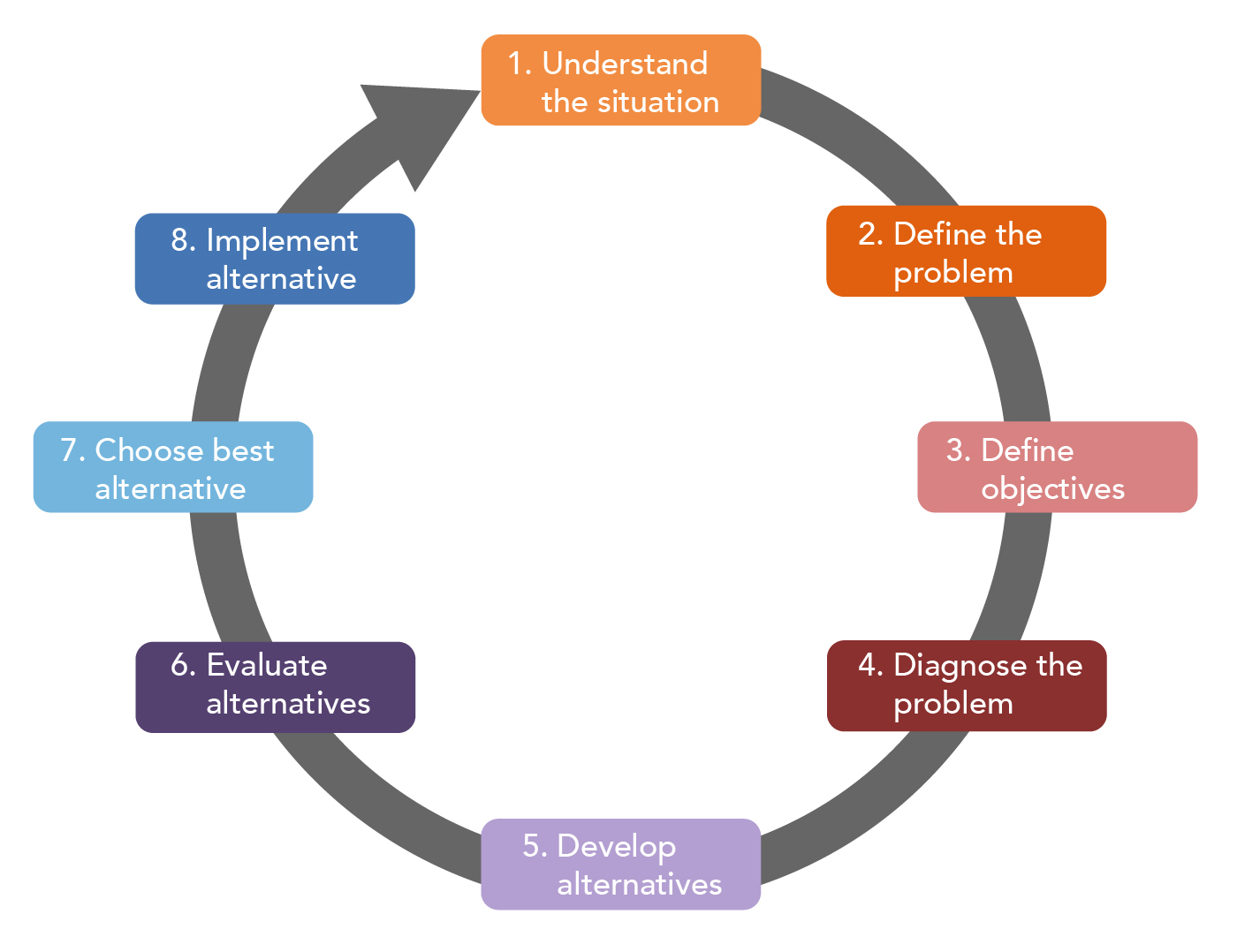
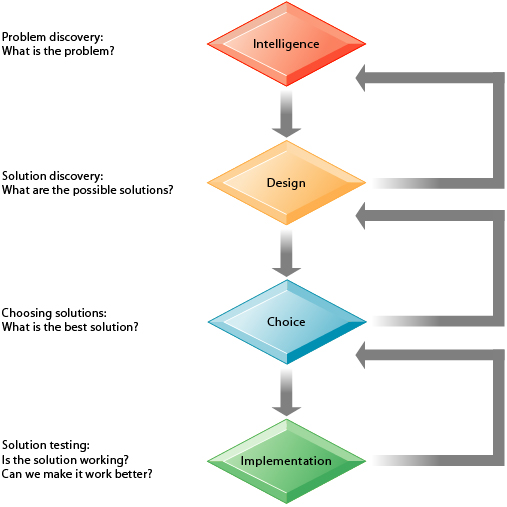
The design phase of decision making consists of discovering identifying and understanding the problems occurring in the organization.

. B have the ability to drill down into lower levels of detail. C easily integrate data from different systems. First-level middle-level and top-level managers.
Strategic misrepresentation - This is a common and often dangerous bias in the organization prevalent at most levels but all-pervasive especially at the strategic level. In traditional organizational structures there are three core levels of decision-making authority. True The intelligence phase of decision making consists of discovering identifying and understanding the problems occurring in the organization.
However most decisions are left to autonomous divisions. TRUE The intelligence phase of decision making consists of discovering identifying and understanding the problems occurring in the organization. Senior managers will ideate and develop the business strategy middle managers will turn the strategy into action plans and line managers will supervise staff as they perform their duties.
The choice phase of Simons decision-making model includes choosing among solution. Middle management faces more. Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower.
Group of answer choices Structured decisions Procedu usman7435 usman7435 02052020 Biology High School answered Which types of decisions are more prevalent at lower organizational levels. Question 8 02 02 pt s A structured decision is repetitive and routine for which known procedures provide solutions. Decision making refers to making choices among alternative courses of actionwhich may also include inaction.
Unstructured c documented d semistructur ed Simons four different stages in decision making are in order from first to last a. There are different types of decision-making at different levels. Senior managers C Analytic modelers D Business analysts E Executives C Operational employees D.
Strategic misrepresentation involves focusing on only the benefits and growth of a strategic decision discarding the costs and risks required. Easily integrate data from different systems D. 3 common organizational patterns for large nonprofits.
Companies operating with decentralized structures often have mid- and lower-level managers making most of the decisions rather than the senior management team. A bureaucratic organization has rigid and tight procedures policies and constraints. A common legal structure known as the multidivisional form or M-form also uses the divisional structure.
Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower organizational levels. Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower organizational levels. TF Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower organizational levels.
In many organizations the number of managers in each level gives the organization a pyramid structure. They are described here to illustrate how IT purchases are made and how system deployments are conducted. A TRUE B FALSE.
Divisional structure in the United States is seen as the second most common structure for organization today. Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower organizational levels. The intelligence phase of decision making consists of discovering.
Since there are many levels decision-making authority has to pass through more layers than flatter organizations. A decentralized organizational structure is one where senior management has surrendered the authority for making certain decisions to the lower levels of the organization. A TRUE B FALSE.
Support the structured decision-making of senior executives B. Senior lawyers also enjoy a. Understand different types of decisions.
BI that is designed to determine the most likely effects of changes in the business environment is called. Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower organizational levels. Have the ability to drill down into lower levels of detail C.
The third stage in Simons description of decision making is implementation. A structured decision is repetitive and routine for which known procedures provide solutions. Group of answer choices Structured decisions Procedural decisions Unstructured decisions Semistructured decisions Operational decisions 1.
In general structured decisions are more prevalent at lower organizational levels and unstructured decision making is more common at higher levels. Here we introduce three models as illustrative stereotypes. They are the prevalent forms for organizing governance across many facets of organizational decision making.
Improving the quality of high-value decision making by an executive will save an organization far more money than improving the quality of lesser-value decisions made at a lower level. Are primarily driven by information derived from a companys transaction processing systems. While it can be argued that management is decision making half of the decisions made by managers within organizations ultimately fail Ireland.
A procedural decisions b Study Resources. Improving the quality of high-value decision making by an executive will save an organization for more money than improving the quality of lesser-value decisions made at a lower level. Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower organizational levels.
CHAPTER 11 Which types of decisions are more prevalent at lower organizational levels. Support the structured decision making of senior executives. Question 7 02 02 pt s Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower organizational levels.
Senior executives face many unstructured decision situations such as establishing the firms five or ten-year goals. Most organizations have three management levels. The whole organization is ultimately controlled by central management.
These managers are classified according to a hierarchy of authority and perform different tasks. Structured decision making is most prevalent at lower organizational levels.
Making Decisions In Different Organizations Organizational Behavior Human Relations
Organizational Decision Making Ispatguru

11 3 Understanding Decision Making Principles Of Management

Pin By Marcelle Ferreira On Dumps In 2021 Dumped Exam Pdf

Levels In Business Hierarchy Hierarchy Business Administration Best Teamwork Quotes

11 3 Understanding Decision Making Principles Of Management

Definition Of Decision Making Decision Making Lesson How To Plan

Afbeeldingsresultaat Voor Agile Organisation Structure Example Organizational Structure Leadership Development Activities Organizational Communication

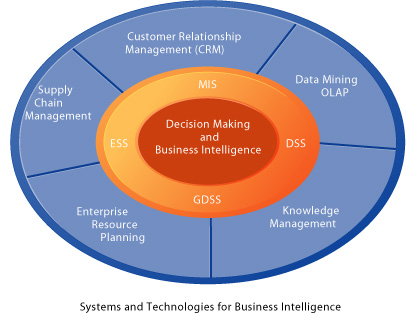
Management Information Systems Chapter 13

Difference Between Centralization And Decentralization With Table Hierarchical Structure Middle Management Senior Management

11 3 Understanding Decision Making Principles Of Management

Amazon Organizational Structure Organizational Structure Organizational Business Development
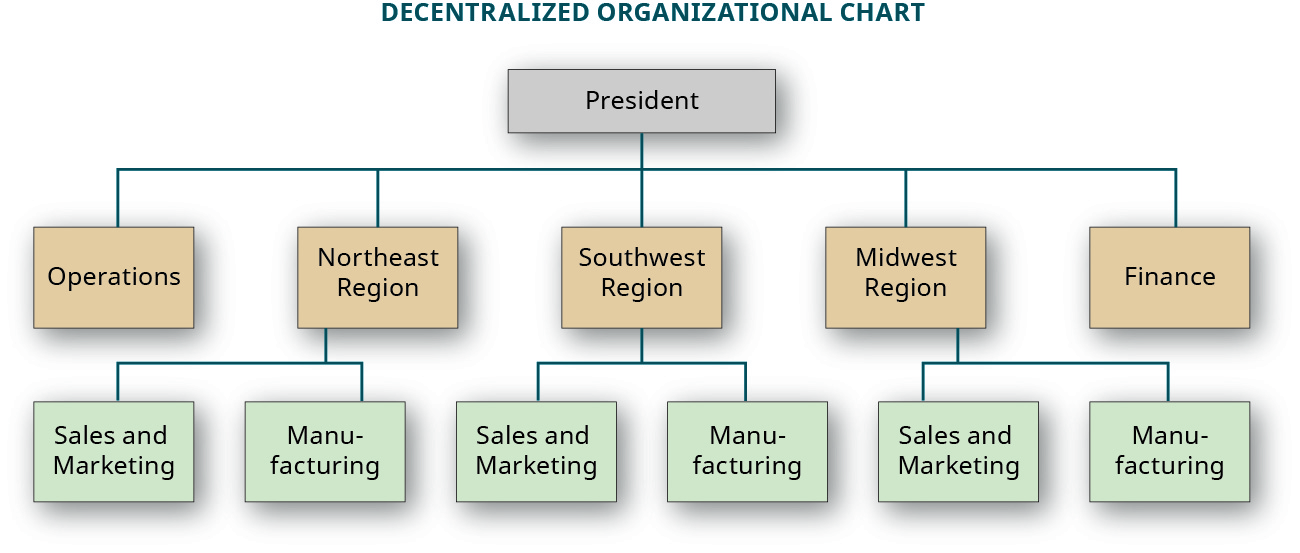
Describe How Decision Making Differs Between Centralized And Decentralized Environments Principles Of Accounting Volume 2 Managerial Accounting

Organization Structure Organizational Design Organizational Structure Improve Communication

Describe How Decision Making Differs Between Centralized And Decentralized Environments Principles Of Accounting Volume 2 Managerial Accounting


Comments
Post a Comment